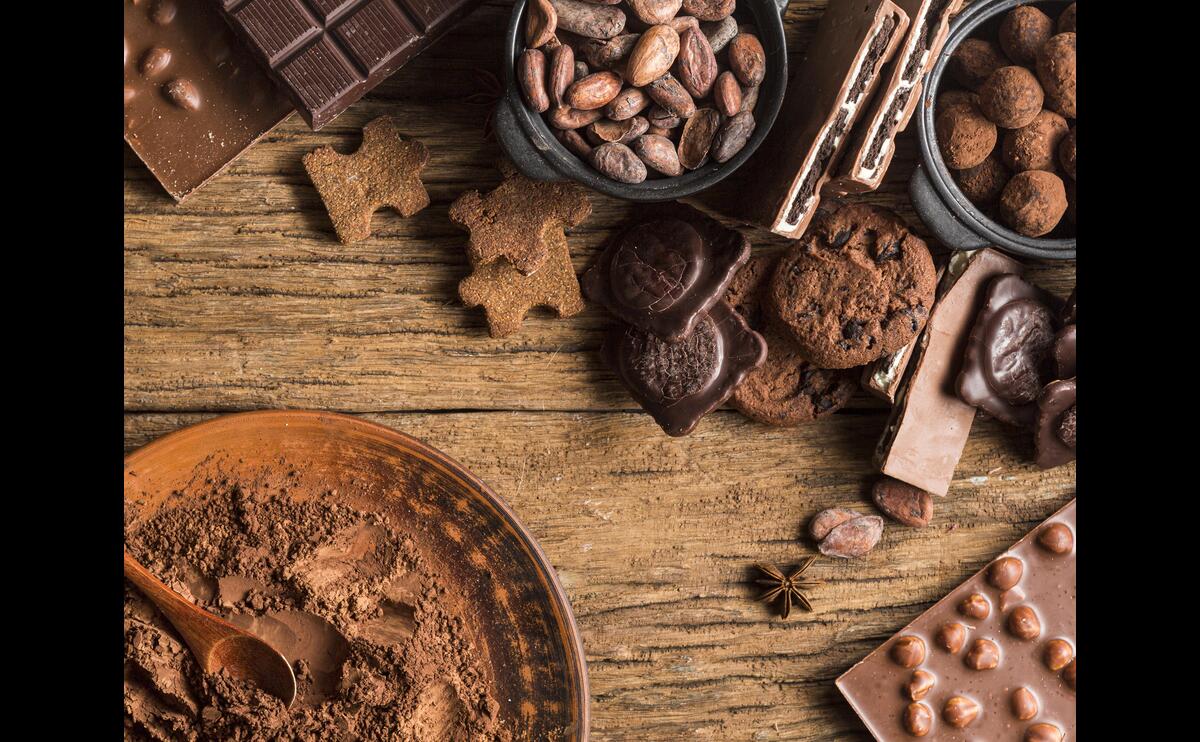
3 Commonly Asked Questions About Chocolate: Does It Spoil, Is White Chocolate Real Chocolate, and Is Dark Chocolate Good for Your Health?
Chocolate is an indispensable treat for many of us. However, questions about its freshness, the differences between varieties, and its health effects still linger. In this article, we will delve into topics such as chocolate’s shelf life, whether white chocolate is real chocolate, and the health benefits of dark chocolate.
1. Does Chocolate Spoil?
Chocolate spoilage is actually quite common. However, the signs of spoilage are usually not mold or rot but a whitish appearance. Here’s what you need to know about chocolate spoilage:
Fat Bloom: When white spots appear on the surface of chocolate, it is typically known as fat bloom. Cocoa butter rises to the surface, creating a white layer, but this does not affect the chocolate’s edibility.
Sugar Bloom: If chocolate is exposed to a moist environment, sugar crystals may form on the surface, leading to a white appearance. While this can affect the texture, the chocolate is still safe to consume.
Shelf Life: Generally, milk and white chocolates have a shorter shelf life because their milk content spoils more quickly. Dark chocolate lasts longer. However, by storing chocolate in a cool, dry place, you can preserve its freshness.
In short, chocolate doesn’t directly mold or rot, but its flavor may change. Therefore, it is important to store chocolate in a cool, dry environment.
2. Is White Chocolate Real Chocolate?
White chocolate has a different composition from traditional chocolate, and many people do not consider it “real” chocolate. This is because white chocolate does not contain cocoa solids.
White Chocolate Composition: White chocolate is made from cocoa butter, milk, sugar, and vanilla, but lacks cocoa solids. Thus, it is made using only cocoa butter, not the cocoa bean itself.
Taste and Texture: White chocolate is sweeter and creamier than other chocolates, primarily due to the large amount of milk and sugar used.
Is it Real Chocolate?: Technically, white chocolate is not considered “chocolate” by some experts because it doesn’t contain cocoa solids, though it does contain cocoa butter, which is derived from cocoa beans. Since it lacks the antioxidant properties of dark chocolate, it is not regarded as real chocolate by chocolate lovers.
In conclusion, while white chocolate can be a tasty option, it does not offer the same health benefits as traditional chocolate.
3. What Are the Health Benefits of Dark Chocolate?
Dark chocolate, known for its high cocoa content and low sugar levels, is recognized for its health benefits. Scientific studies support its positive effects:
Antioxidant Content: Dark chocolate contains powerful antioxidants, such as flavonoids, which help reduce cell damage and may delay aging.
Heart Health: The flavonoids in dark chocolate can improve circulation and help lower blood pressure, which has a positive effect on heart health.
Brain Health: The caffeine and theobromine in dark chocolate can support brain function. Studies suggest that dark chocolate may help improve cognitive function and focus.
The Source of Cocoa Beans, Taste Profiles, and the Effect of Natural Sweeteners on Chocolate The unique flavor of chocolate actually comes from the cocoa bean, which has a long history. The cocoa beans used in chocolate production come from different geographical regions, each offering distinct taste profiles. Additionally, natural sweeteners and additives play a significant role in the flavor and texture of chocolate. This article will explore the key details involved in chocolate production, from the origins of cocoa beans to taste profiles, natural sweeteners, and additives.
1. The Origin and Sources of Cocoa Beans
The cocoa bean originates from the tropical regions of the Amazon and Central America. Today, most cocoa production occurs in countries along the equatorial belt. The region where the cocoa beans are grown directly influences the taste and texture of the chocolate. Here are some important cocoa production regions and their taste profiles:
South American Cocoa Beans: Cocoa beans from countries like Ecuador, Peru, and Venezuela typically have a fruity acidity and subtle floral aromas. The chocolates made from these beans are characterized by tropical fruit notes and light spice aromas.
African Cocoa Beans: Countries such as Ghana and Ivory Coast provide a large portion of the world’s cocoa. These beans have richer, earthier, and nutty taste profiles. African-origin chocolates are known for their creamy texture and caramel notes.
Asian Cocoa Beans: Cocoa beans grown in countries like Indonesia and the Philippines offer spiced and intense flavors. Asian-origin chocolates tend to feature smoky and earthy notes.
This diversity highlights the importance of selecting the right cocoa beans in chocolate production. The region of origin directly influences the quality and flavor of the chocolate.
2. Taste Profiles and Cocoa Content in Chocolate
Cocoa beans not only provide flavor but also contribute texture and aroma to chocolate. The higher the cocoa content, the more intense and sharp the flavor becomes. Here’s a breakdown of taste profiles based on cocoa content:
70% and Above Cocoa Content: These chocolates, known as dark chocolate, offer a strong cocoa flavor. They have a bold and sharp aroma due to the presence of cocoa butter and cocoa solids.
50-70% Cocoa Content: Often referred to as semi-dark, these chocolates offer a balanced flavor with distinct cocoa notes but a slight sweetness.
20-50% Cocoa Content: Found in milk chocolates, these chocolates are softer and sweeter with a lighter taste profile due to the lower cocoa content.
The cocoa content in chocolate directly impacts its taste, so chocolate manufacturers carefully control this aspect. Higher cocoa content provides a sharper flavor, while lower cocoa content results in a sweeter, milder experience.
3. Natural Sweeteners and Improving Chocolate Flavor
To balance the flavor and ensure a natural sweetness, natural sweeteners are often used in chocolate. Here are some common natural sweeteners used in chocolate production:
Honey: As a natural sweetener, honey enhances the sweetness of chocolate while imparting a subtle floral aroma. It is often used in organic and healthy chocolate varieties.
Date Syrup: A more natural alternative to refined sugar, date syrup adds a caramel-like flavor to chocolate. Its sweetness is intense but does not overpower the cocoa taste.
Maple Syrup: Often used in dark chocolates, maple syrup provides natural sweetness and imparts a mild woody flavor.
Natural sweeteners are healthier than artificial sugars and contribute to the flavor profile of chocolate without masking its natural aroma.
4. Additives and Their Effect on Chocolate
Some chocolates contain additives to enhance flavor and extend shelf life. However, the correct proportion and quality of additives must be maintained, as excessive use can affect the chocolate’s quality:
Lecithin: An emulsifier that improves the consistency of chocolate. Soy lecithin is commonly used to make the chocolate smoother. Excessive use can negatively affect the flavor.
Preservatives: Certain preservatives may be added to extend the shelf life of chocolate. However, chocolates containing additives often have a lower quality compared to those made with natural ingredients.
Flavors and Sweeteners: Additional flavors like mint, vanilla, and coffee can be added to enhance chocolate’s taste. While these enrich the flavor profile, they may alter the natural cocoa taste.
To choose high-quality chocolate, it’s important to review the ingredient list. The fewer additives, the more natural the chocolate.
Conclusion
Several factors influence the flavor of chocolate, from the origin of the cocoa beans to the natural sweeteners and additives. Natural sweeteners enhance the flavor without overpowering the chocolate’s natural aroma, while additives may help extend shelf life. However, to ensure the most natural and high-quality chocolate, it’s crucial to pay attention to the ingredient list.
“It suggests that chocolate may have positive effects on memory and concentration.”
“Happiness Hormone: Dark chocolate contains phenylethylamine, a substance that can boost serotonin, the happiness hormone, potentially improving mood. When consumed during stressful moments, it has a positive effect on mood.”
“However, to reap the benefits of dark chocolate, it is important to choose chocolates with 70% or higher cocoa content and consume them in moderation, such as a few pieces per day.”